Introduction
해당 논문은 temporal action detection task 를 위한 논문이다. temporal action detection 이란 비디오에서 action 영역의 시작과 끝을 (SSD의 bounding box)같이 localization과 classification을 진행하는 것이다. 해당 논문은 action detection 의 성능을 높이기 위하여 video에서 action 영역을 표기한 temporal annotation을 최대한 활용하여 multi-task 모델의 이점을 통해 main task인 temporal action detection의 성능을 높인다. THUMOS14, Charades, ActivityNet 3가지 논문에서 진행한 실험을 공개하였으며 일관성 있는 결과를 보였다. 해당 논문은 사용할 수 있는 annotation을 최대한 활용하여 기존에 널리 사용되던 모델에서 일관성 있는 성능 향상을 보였으며, annotation 활용을 위해 2가지 auxiliary task (보조 과제)를 설계하였다. 이 논문의 contribution을 정리하면 다음과 같다.
- label이 부족한 video 분야에서 label 부족으로 인한 문제를 완화하고
- annotation을 재활용 하여 multi-task 방식으로 detection 성능을 높이고
- THUMOS14, Charades, ActivityNet 3가지 데이터셋에서 일관적으로 해당 방식의 효과를 보였다.
해당 논문은 video 분야에서 detection 성능을 높이기 위한 새로운 시각을 가설로 세우고 실험으로 검증하여 contribution을 주었다고 생각한다.
method
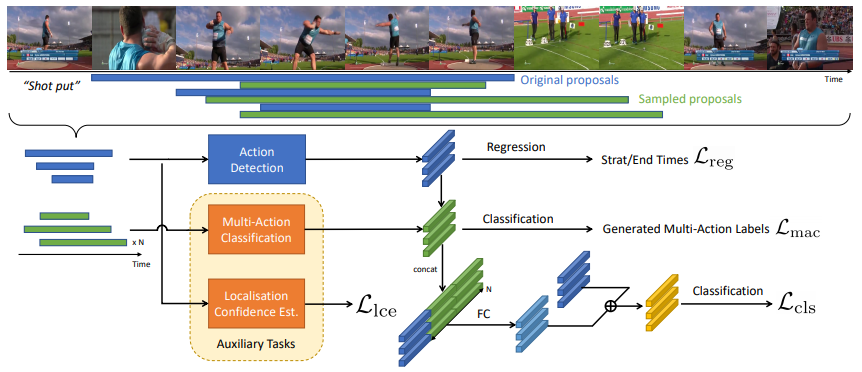
- Pretext Task Design
해당 논문은 annotation을 재활용할 auxiliary task로 Multi-Action Classification과 Localisation Confidence Estimation을 선정했다. action detection을 위한 annotation은 action의 카테고리와 위치를 제공한다. Multi-Action Classification에서는 각 비디오에서 다양한 action들이 발생할 확률(video 내에서 해당 action이 차지하는 비율)을 soft label로 이용하였다. 다음으로 ground truth segments의 모호성 (annotation의 시작과 끝이 annotator마다 모호함) 에 대응하기 위하여 이에 적합한 Localisation Confidence Estimation task를 적용하였다고 한다. 두 task 모두 action detection의 annotation을 재활용하여 추가적 정보 없이 구성할 수 있다. - training
학습은 두단계로 나누어 refining을 진행한다. 일반적인 multi task 학습처럼 모든 task를 join상태로 학습 한 뒤, refining 고정에서는 pretext task 중 Multi-Action Classification의 결과를 main task인 detection시 활용한다. 그 수식은 다음과 같다. refineing을 x를 x’으로 변경하는 과정이라 할 때, 식1과 같이 정의되며 W는 projection matrix이며 t는 x의 후보가 되는 각각의 temporal windows이다.
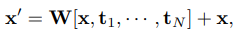
Experiments
앞서 언급하였듯 해당 논문은 THUMOS14, Charades, ActivityNet 3가지 데이터셋에서 실험을 진행하였으며 제안하는 방식을 통한 성능 향상을 일관적으로 보였다. 아래는 각 데이터셋에 대한 3가지 ablation study이다. task 1은 Multi-Action Calssification, task 2는 Localisation Confidence Estimation 이며, 모든 데이터 벤치마크에서 task 1이 task 2보다 도움이 되며, 두 task를 각각 사용하는 것 보다 같이 사용했을때 성능향상이 가장 큼을 보이면서 제안하는 방식이 실제로 일관성 있게 성능 향상에 도움이 됨을 보였다.
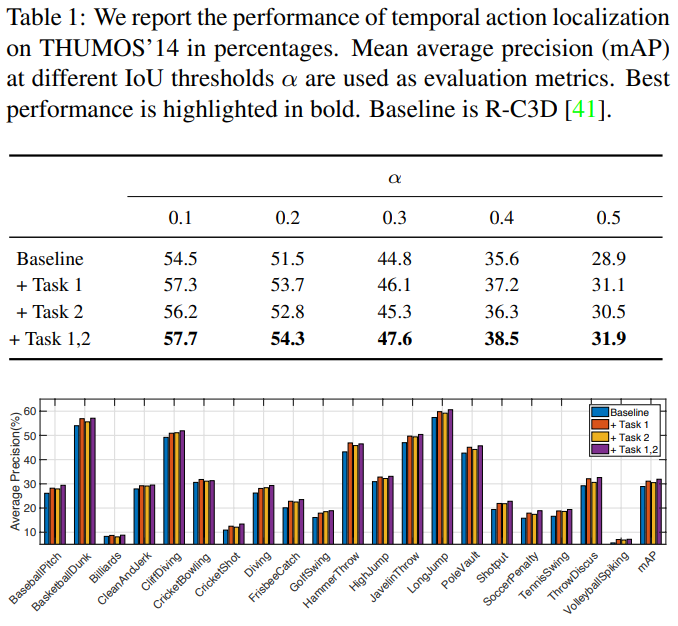
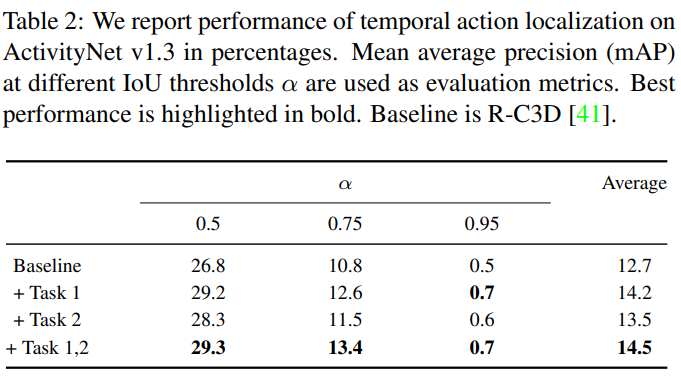
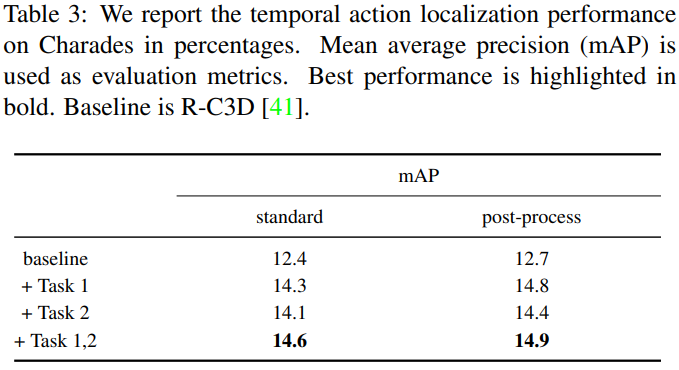
또한 앞서 언급하였듯이 기존에 널리 사용되던 모델에 두 auxiliary task 를 적용하여 성능 향상을 보였으며 그 실험은 다음과 같으며 성공적으로 적용할 수 있음을 보인다.
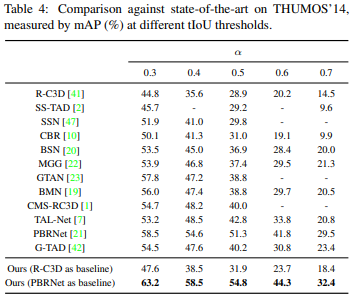
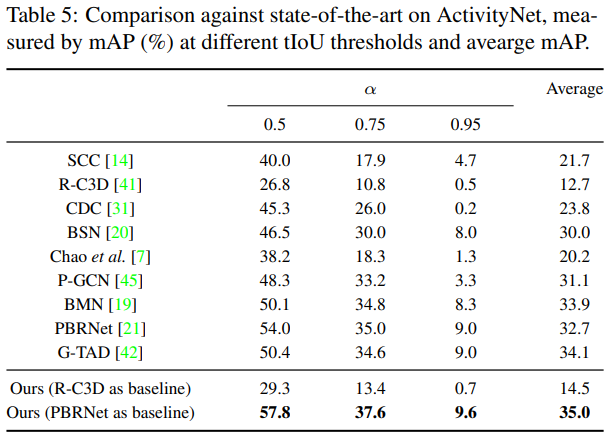
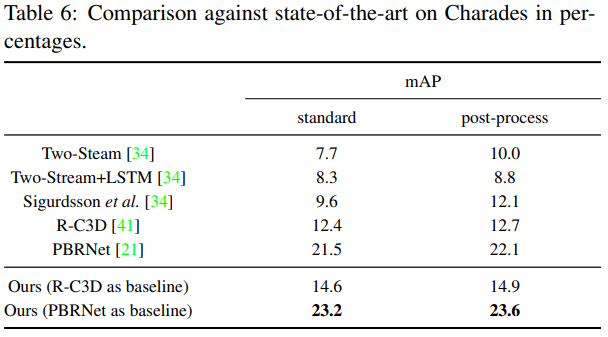
total loss 계산은 어떻게 되는건가요?