Abstract
Convolutional network는 end-to-end, pixel-to-pixel로 학습된다. 이 논문의 핵심은 input 사이즈에 영향을 받지 않는 “fully-convolutional” networks를 만드는 것이다. 기존의 분류 네트워크들을 fully convolutional networks로 바꾸고 fine-tuning을 하여 segmentation task에 맞췄다. 그리고 deep, coarse layer에 정확하고 자세한 segmentation을 위해 shallow layer를 결합하는 skip architecture를 이용한다.
Introduction
FCN은 end-to-end, pixel-to-pixel로 학습된다. dense feedforward 계산과 backpropagtion에 의해 학습과 추론이 전체 이미지에서 동시에 일어난다. upsampling layer와 subsampled pooling이 픽셀 단위의 예측과 학습을 가능하도록 한다. 이 논문의 방식은 superpixels, proposals, post-hoc refinement 등의 복잡한 pre, post-processing이 필요 없다.
semantic segmentation은 global information으로 무엇(what), local information으로 어디(where)인지 푼다. deep feature hierarchies는 location와 semantics가 암호화 되어있다. (논문의 문장이 잘 해석이 안됨..) 논문은 skip architecture을 이용해 deep,coarse한 semetic 정보에 shallow, 미세한 외관 정보를 결합한다.
Fully convolutional networks
각 레이어는 h * w * d (d: feature or channel dimension) 이고 첫번째 레이어는 이미지로 d는 색 채널이 된다. convolutional network는 input 이미지에 의해 각각의 구성 요소들(convolution, pooling, activation function)이 결정된다.
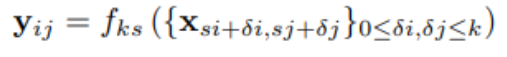
k : 커널사이즈, s: stride/subsampling factor, f_ks : layer type
Adapting classifiers for dense prediction
기존의 모델은 fully connected layer로 인해 input 사이즈가 고정되어있었고 non-spatial(공간 정보가 사라진)한 output을 산출한다. 이러한 fully connected layer가 전체 영역을 보는 kernel을 이용하면 convolution으로 볼 수 있다.
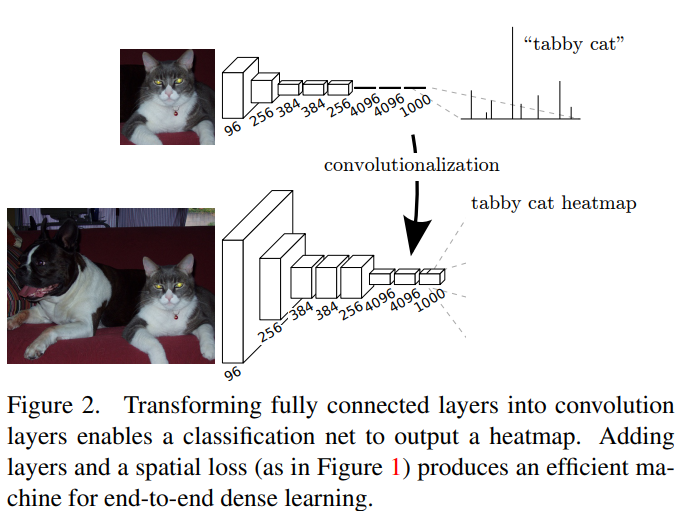
subsampling으로 인해 output 차원이 줄어들었던 기존의 모델과 다르게 fully convolutional로 바꾼 결과는 어떠한 크기의 input에도 output map을 만들수 있다. 분류 모델에서 subsample은 filter를 작게 만들어 연산을 합리적으로 할 수 있게 한다. 이로인해 output이 coarse하게 만들어지고, input은 receptive field의 픽셀 stride와 같은 크기로 줄어든다.
Upsampling is backwards strided convolution
coarse ouput과 dense pixel을 연결하는 방법은 interpolation이다. f는 stride가 1/f인 convolution 의 일종으로 볼 수 있고, output stride가 f인 backward convoluion(deconvolution) 이다. deconvolution 필터는 크기가 고정될 필요가 없이 학습될 수 있다. 심지어 deconvolution layer와 activation 함수를 쌓으면 nonlinear upsampling으로 학습할 수 있다.
Patchwise training is loss sampling
전체 이미지의 fully convolutional 학습은 batch가 전체 receptive field로 구성된 patchwise학습과 동일하지만 가능한 batch의 수를 더 줄여 효율적이다. fully convolutional 학습에서 class balance는 weighting the losss로 해결할 수 있고 loss sampling을 spatial correlation에 사용할 수 있다.
Segmentation Architecture
ILSVRC의 분류기들을 in-network upsampling과 pixelwise loss를 이용해 FCNs로 바꾸고, segmentation을 위해 fine-tuning했다. 그 다음 skips를 이용해 coarse, semantic과 local, appearance정보를 가진 layer를 fuse했다. 이 skip구조는 esmantics와 output의 spatial precision을 위해 end-to-end로 학습된다.
From classifier to dense FCN
AlexNet, VGG-16, GoogLeNet을 이용했다. 이때 GooLeNet은 마지막 average pooling층을 버리고 사용했다. 각 네트워크에서 마지막 분류층을 버리고 모든 fully connected layer를 (class 개수, 이 논문은 pascal voc를 이용해서 21)11의 convolution으로 바꿨다. 그 뒤에는 deconvolution layer로 coarse output을 upsamling했다.
Combining what and where
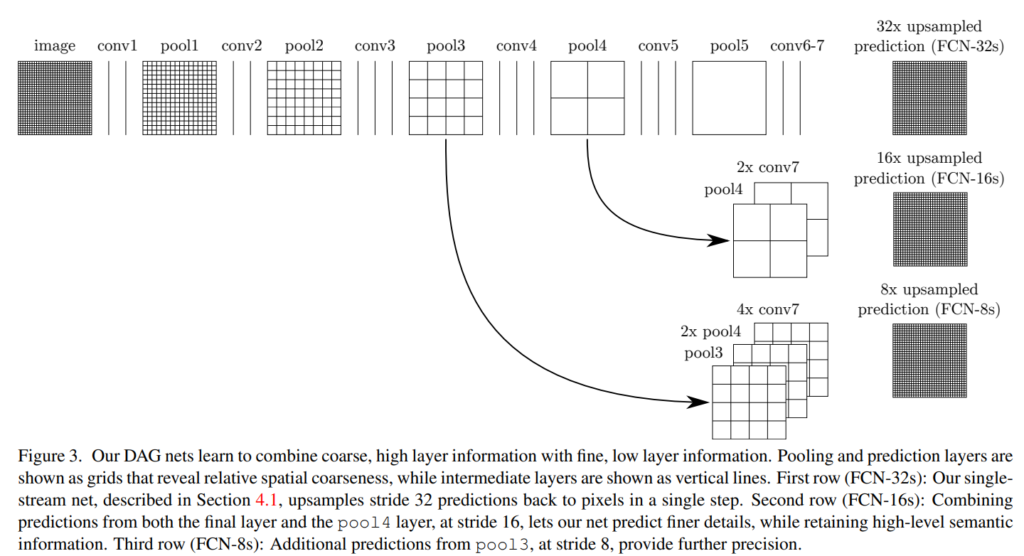
마지막 prediction layer에서 stride가 32인 upsampling은 output의 detail을 제한한다. 그래서 마지막 예측 layer에 lower layer들을 skip해서 합치는 방법으로 output의 detail을 더 잘 나타내고자 한다.
pool 4와 conv7(fully connected → fully convolution된 레이어)의 2 x upsampling을 fuse한 것의 prediction과 16 x upsampled prediction을 합치고, pool3과 pool4의 2 x upsampling과 conv 7의 4 x upsampling을 fuse한 것의 prediction과 8 x upsampled prediction을 합친다.
Experimental
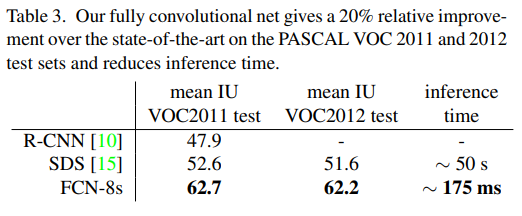
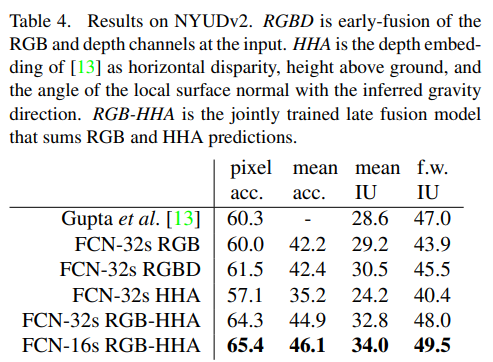
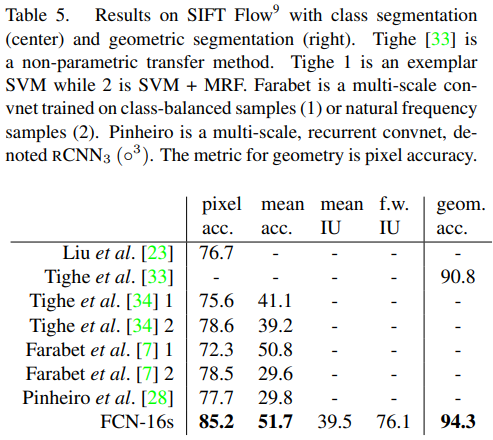
RCN-AlexNet, FCN-VGG16, FCN-GoogLeNet을 실험했다. original classifier nets에는 dropout이 사용되었다. image classifier를 segmentation에 맞도록 fine-tuning을 해서 사용했다. 데이터셋은 PASCAL VOC 2011 and 2012, NYUDv2, SIFT Flow를 사용하였다.
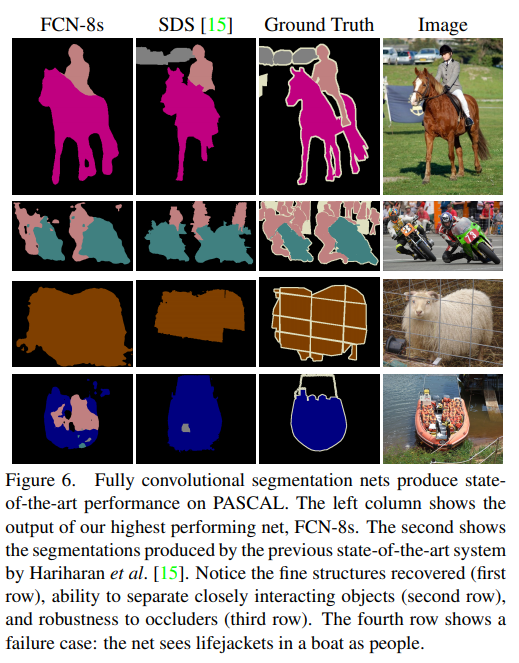
Conclusion
fully convolutional network는 분류 convnet의 특별한 경우이고 구조 개선과 여러 resolution의 결합하여 분류를 segmentation으로 확장하면 학습과 추론을 단순화 하고 속도 향상과 좋은 성능을 얻을 수 있다.
요약
- 기존의 calssification net은 input size가 정해져 있고, fully connected layer가 있어서 공간적 정보가 손실되는 문제가 있다.
- fully connected layer를 1*1 인 필터를 이용해 fully convolutional layer로 만들면 공간적 정보도 유지하고 input size에 유연하게 대처할 수 있다.
- output이 coarse map으로 픽셀 단위의 dense prediction을 하기에는 부족해 upsampling이 필요하다.
- upsampling 방식은 bilinear interpolation과 backward convolution(deconvolution)방법이 있고 deconvolution을 이용하면 upsampling도 학습할 수 있다.
- 이렇게 coarse map을 upsampling했지만 deep layer의 정보를 이용한 것으로 appearance 정보가 부족해서 skip architecture를 이용해 deep,coarse한 semetic 정보에 shallow, 미세한 외관 정보를 결합하는 방식을 이용해 더 정확한 예측을 할 수 있다.
official code : http://fcn.berkeleyvision.org
논문 : Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation (cv-foundation.org)
마지막 prediction layer에서 stride가 32인 upsampling은 output의 detail을 제한한다. 그래서 마지막 예측 layer에 lower layer들을 skip해서 합치는 방법으로 output의 detail을 더 잘 나타내고자 한다.
이 부분은 단순히 실험적으로 발견한 것인가요 ??
실험적으로 발견한 것인지 이론적으로 발견한 것인지는 정확히 모르겠습니다. 하지만 downsampling을 여러번 거친 coarse map을 이용해 upsampling하는 것이므로 실제 이미지의 외관 정보와는 다를 수 있고 이를 보완하기 위해 skip을 이용한 것이기 때문에 단순히 실험적으로 발견한 것이 아니고 이론적으로 고려한 사항일 수도 있을 것 같습니다.
안녕하세요 승현님! Combining what and where 부분에서 detail을 살리기 위해 lower layer를 skip해서 합쳐줬는데 pool3 과 pool4만 이용한 이유가 있을까요? pool2도 사용한다면 더 detail한 부분을 가져올 수 있을 것 같은데 pool3까지만 사용한 이유가 궁금합니다!
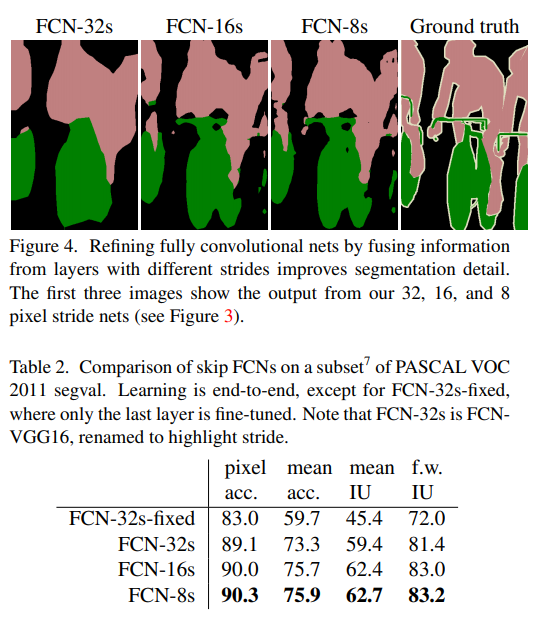
저자들에 따르면, Figure4의 그림으로 확인할 수 있듯이, FCN-32s→16s→8s 순으로 보았을 때, pool3까지 이용하였을 원하는 만큼의 개선을 이루었고 점차 개선되는 정량적 수치(Table2) 감소하였기 때문에 추가적인 pool 레이어를 이용하지 않았다고 합니다.